Case Study
DATRON leverages QuestDB for high-volume time-series data
DATRON migrated from InfluxDB to QuestDB to handle their data ingestion requirements and reduce costs.
- High-throughput ingestion
- Achieving superior performance with high-frequency sensor data.
- Out-of-the-box solution
- Docker image for easy and turnkey deployment.
- Cost reduction
- QuestDB allowed DATRON to do more with less hardware.

- Avg ingested rows/sec
- 3M+
- Write speed vs InfluxDB
- 10x
- Compression ratio
- 6x
- Cloud up-time
- 99.99999%
Real-Time Monitoring
High-volume sensor data management
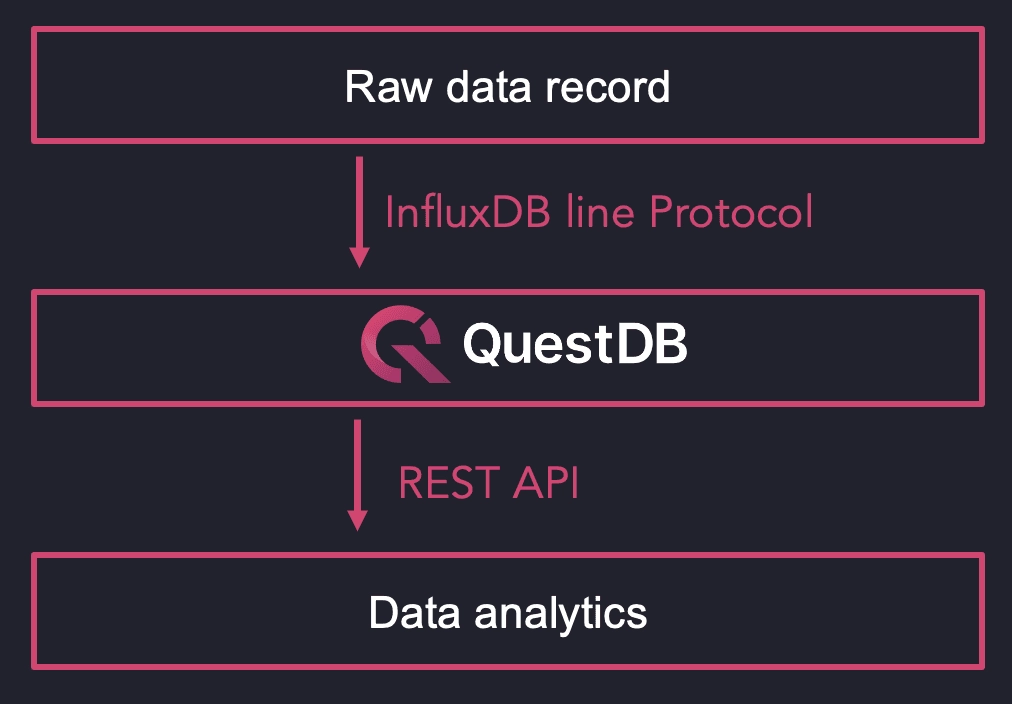
DATRON uses QuestDB to store and analyze high-frequency sensor data from their CNC machines. Their setup ensures continuous monitoring with massive ingestion rates at the data layer.
- High-Performance Data Store
- QuestDB efficiently handles high-throughput time-series data.

"QuestDB offers new possibilities while reducing costs and simplifying data analysis at DATRON."
Tim Borowski
Lead Developer, DATRON
High-performance CNC data ingestion
Effortless high-throughput data handling
DATRON uses QuestDB for CNC sensor data with superior performance.

- Out-of-the-box solution
- Deploy QuestDB effortlessly using Docker.
- SQL capabilities
- Powerful querying with native time-series SQL extensions.
- Optimized for ingestion
- QuestDB efficiently ingests high-frequency data.